Understanding Adhesive Capsulitis of Left Shoulder
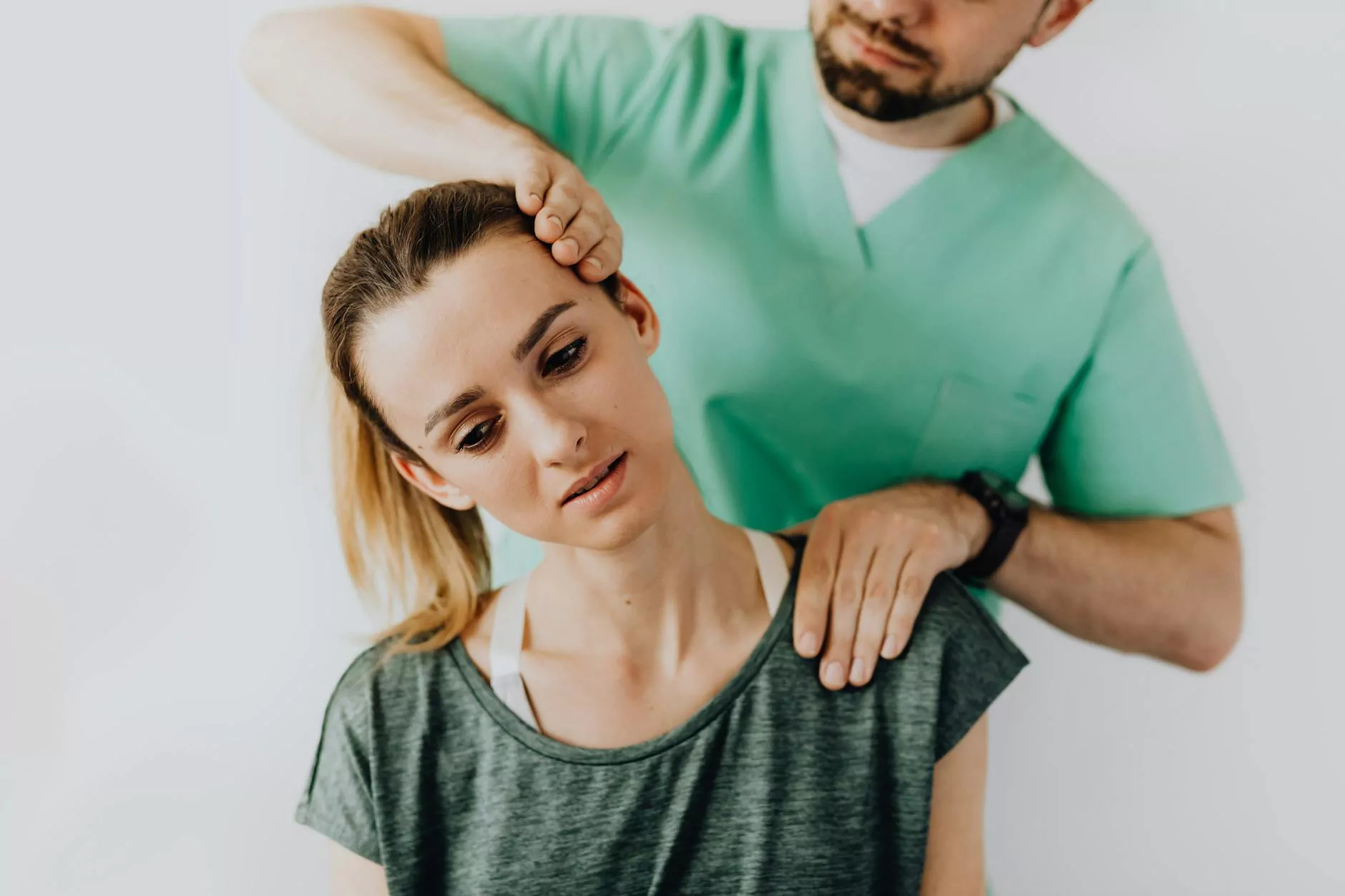
Adhesive capsulitis of left shoulder, commonly referred to as frozen shoulder, is a painful and often debilitating condition that affects the shoulder joint. This medical phenomenon occurs when the capsule surrounding the shoulder joint becomes inflamed and thickened, leading to stiffness, significant discomfort, and a limited range of motion. In this article, we delve into everything you need to know about this condition, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Adhesive Capsulitis?
Adhesive capsulitis is characterized by the progressive loss of mobility in the shoulder joint, often with a distinct onset of pain. This condition can affect anyone but is more common in people between the ages of 40 and 60, with women being more susceptible than men. There are typically three stages associated with adhesive capsulitis, each presenting unique challenges and experiences.
The Stages of Adhesive Capsulitis
- Freezing Stage: In this initial stage, individuals begin to experience a gradual shoulder stiffness. Movement becomes increasingly painful, and inflammation heightens.
- Frozen Stage: This stage involves a marked reduction in shoulder movement. Pain may persist, yet it tends to diminish during this phase. The shoulder's range of motion continues to be severely limited.
- Thawing Stage: The final stage, wherein the shoulder’s range of motion begins to improve gradually. This phase can last for months, as shoulder function returns to normal.
Causes of Adhesive Capsulitis
The exact cause of adhesive capsulitis of left shoulder remains largely unknown, but several factors may potentially contribute to its development. Some of these include:
- Injury or Trauma: A recent injury or surgery affecting the shoulder can increase the risk.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and Parkinson’s disease have been linked to a higher incidence of frozen shoulder.
- Prolonged Immobility: Extended periods of shoulder immobility due to injury can lead to the development of adhesive capsulitis.
- Age and Gender Factors: Individuals over the age of 40, particularly women, are at a higher risk.
Symptoms of Adhesive Capsulitis
Identifying adhesive capsulitis is crucial for timely intervention. The primary symptoms associated with this condition are:
- Severe Pain: Individuals often describe the pain as sharp and debilitating, particularly when moving the arm.
- Limited Range of Motion: Patients typically find it challenging to perform everyday activities such as reaching overhead, behind the back, or performing simple tasks.
- Stiffness: Constant stiffness in the shoulder joint that limits motion.
- Discomfort at Night: Symptoms may worsen during nighttime, affecting sleep quality.
Diagnosis of Adhesive Capsulitis
When diagnosing adhesive capsulitis, a healthcare provider typically conducts a physical examination and reviews the patient’s medical history. They may also recommend imaging tests, such as:
- X-rays: To rule out other potential causes of shoulder pain and immobility.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): To provide detailed images of the shoulder's soft tissues.
Treatment Options for Adhesive Capsulitis
Treating adhesive capsulitis can be challenging, but several approaches can help alleviate symptoms and restore shoulder mobility. These include:
Conservative Management
Most patients begin with conservative treatment options, such as:
- Physical Therapy: Involves stretched range of motion exercises aimed at regaining mobility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Hot/Cold Therapy: Applying heat or ice can aid in relieving pain and promoting relaxation in shoulder muscles.
Advanced Interventions
For those who do not respond to conservative treatments, advanced options may be considered:
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Shoulder Manipulation: Under anesthesia, a healthcare provider manipulates the shoulder joint to break up adhesions.
- Surgery: In rare cases, arthroscopic surgery may be required to remove scar tissue from the shoulder joint.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehab is a crucial part of the recovery process. Following any treatment, a structured rehabilitation regime will help restore mobility. Key aspects include:
- Gradual Exercises: Initiating shoulder exercises as directed by a physical therapist.
- Consistency: Regular participation in rehabilitation can significantly improve outcomes.
- Patience: Recovery can take several months, and it's important to remain patient and consistent with exercises.
Living with Adhesive Capsulitis
Dealing with adhesive capsulitis of left shoulder can be challenging, particularly as the condition can impact daily activities. Here are some tips to manage life with adhesive capsulitis:
- Seek Support: Engaging with family and friends can provide emotional relief.
- Adapt Activities: Modify daily tasks to accommodate shoulder limitations.
- Stay Informed: Knowledge about the condition can empower patients to make better decisions regarding their healthcare.
Conclusion
Adhesive capsulitis of left shoulder, or frozen shoulder, is a complex condition that can affect both physical movement and overall well-being. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options can help individuals manage their condition effectively. If you suspect that you are suffering from adhesive capsulitis, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plan.
Remember, with timely intervention and proper management, the journey to recovery from adhesive capsulitis can lead to restored mobility and a return to normal activities. Don't hesitate to reach out for professional support in managing this condition effectively.









